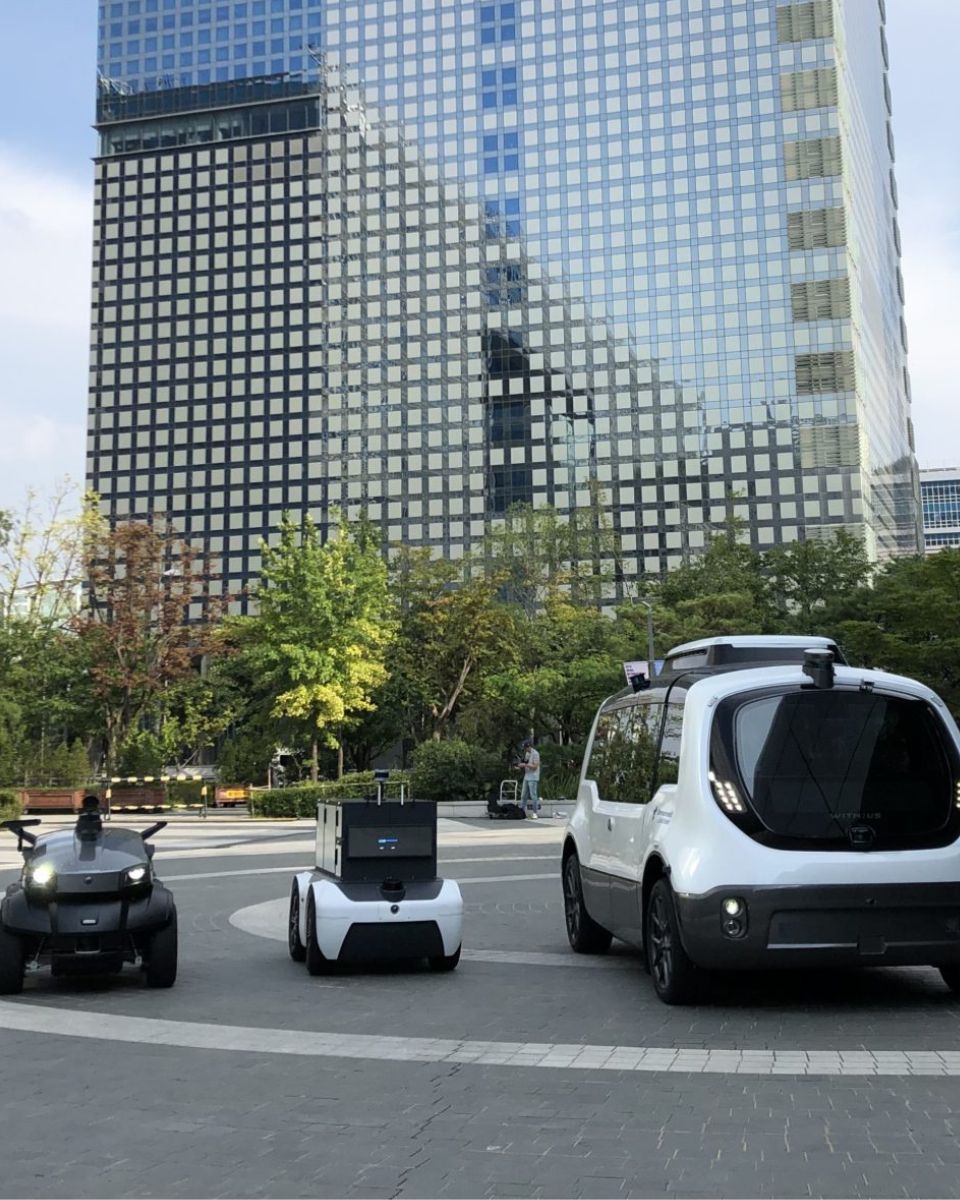
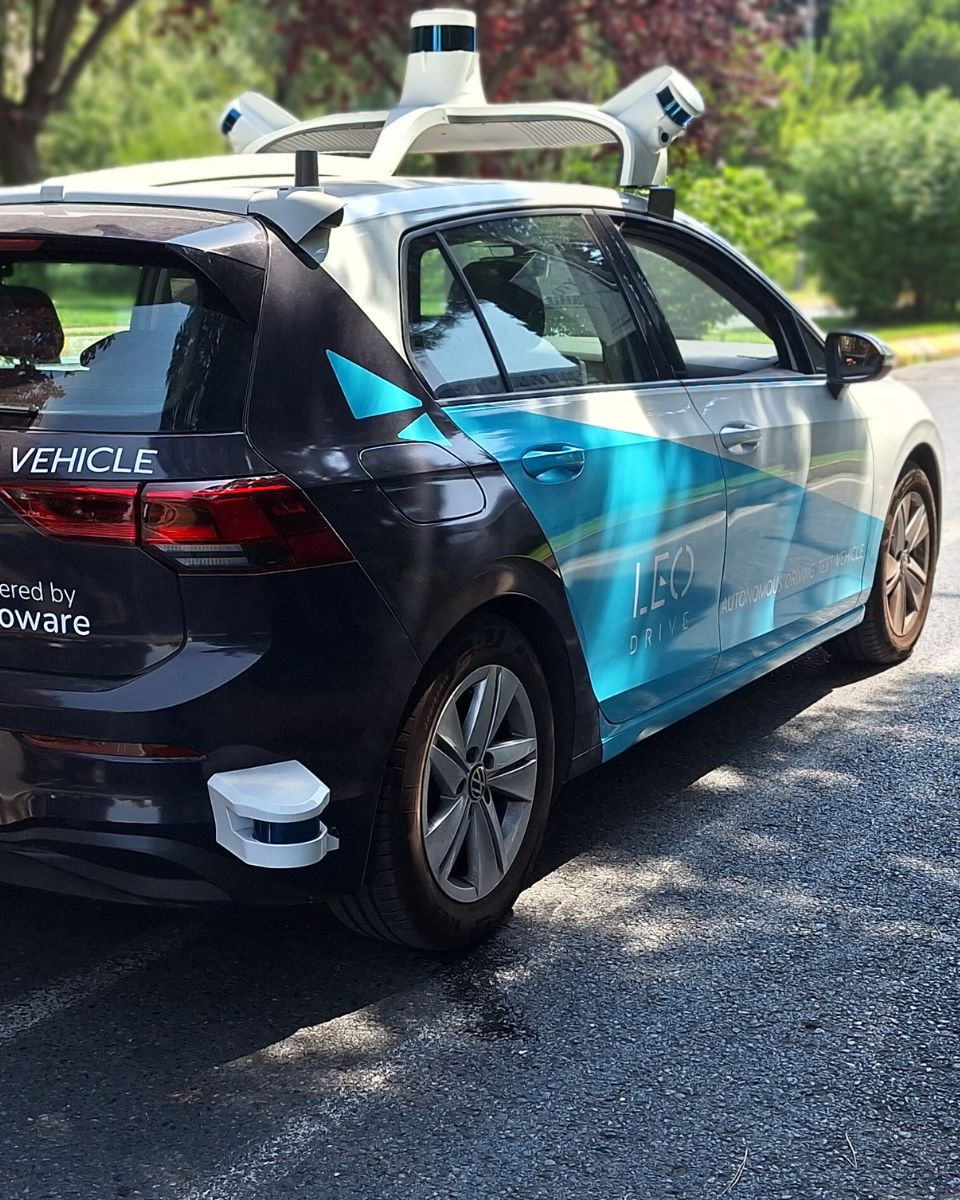
Accurate navigation & positioning for autonomous vehicles
Our motion and navigation sensors offer numerous advantages for Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles, contributing to enhanced safety, precision, and performance. These sensors integrate advanced technologies like Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) to provide real-time, highly accurate data on vehicle positioning, motion, and orientation, even in challenging environments.
We are renowned for our expertise in sensor engineering, extensive calibration techniques, and filtering algorithms. Our INS, combine data from accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GNSS to provide highly accurate and reliable positioning information.
Our technology is cornerstone to map the roads and surroundings with high accuracy and allow vehicles to navigate complex environments, accurately follow predefined routes and operate safely.

Enhanced sensor fusion and reliable performance in all conditions
Our sensors are designed to seamlessly integrate with other systems like LiDAR, radar, and cameras, creating a comprehensive sensor fusion platform. Combining data from multiple sensors ensures more accurate mobile mapping. When one system encounters an issue, such as GNSS signal loss, inertial sensors maintain reliable vehicle position, improving safety and resilience.
Autonomous and ADAS technologies require consistent performance regardless of environmental conditions. All our sensors are engineered for robust operation in harsh environments (temperatures and vibrations) and complex GNSS areas where our INS solutions ensure continuous navigation when satellite signals reception is challenged entering tunnels, parking garages, or driving in urban areas around tall buildings.
Enhancing localization and map-matching accuracy
Our inertial navigation systems use accelerometers and gyroscopes to calculate the vehicle’s position, velocity, and orientation by dead reckoning—independently of GNSS.
When paired with GNSS in a tightly coupled sensor fusion algorithm, it provides a continuous, highly accurate trajectory, even during GNSS outages.
With an integrated INS+GNSS system, the INS keeps a steady path even when signals are lost, providing accurate directions and location data to help the vehicle align with the correct road segment on the HD map. The combined system stops you from going the wrong way, missing exits, or doing unsafe manoeuvres because of localization errors.
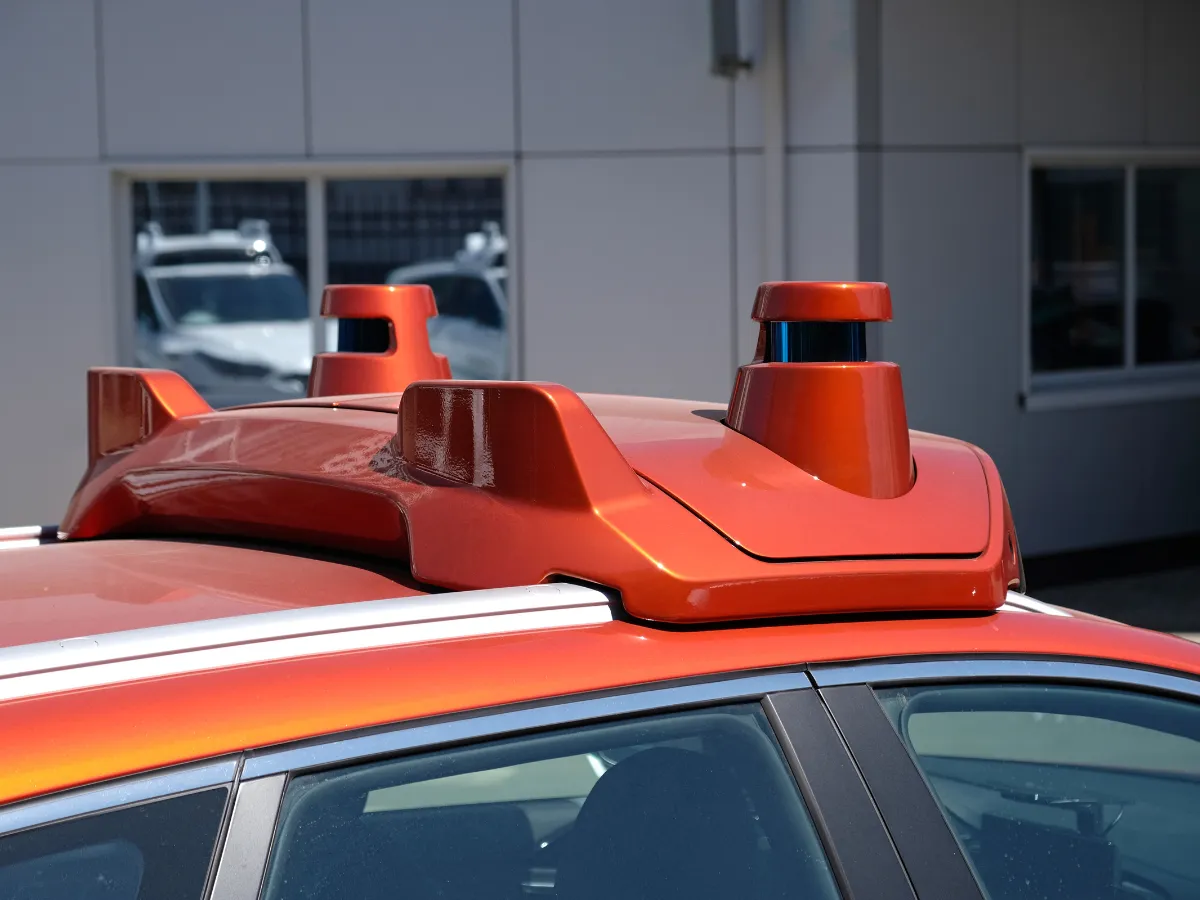

Solutions for ADAS systems
Our GNSS/INS sensors deliver accurate position, velocity, and orientation data in real time, ensuring reliable performance even in urban canyons or tunnels. With robust calibration, low latency, and easy integration, our solutions support safer, smarter, and more autonomous vehicles or ADAS systems.
Vehicles application brochure
Our brochures provide comprehensive insights to meet your needs. Designed to be both informative and engaging, they serve as a valuable resource for customers, partners, and stakeholders alike.
Explore other autonomous vehicles applications
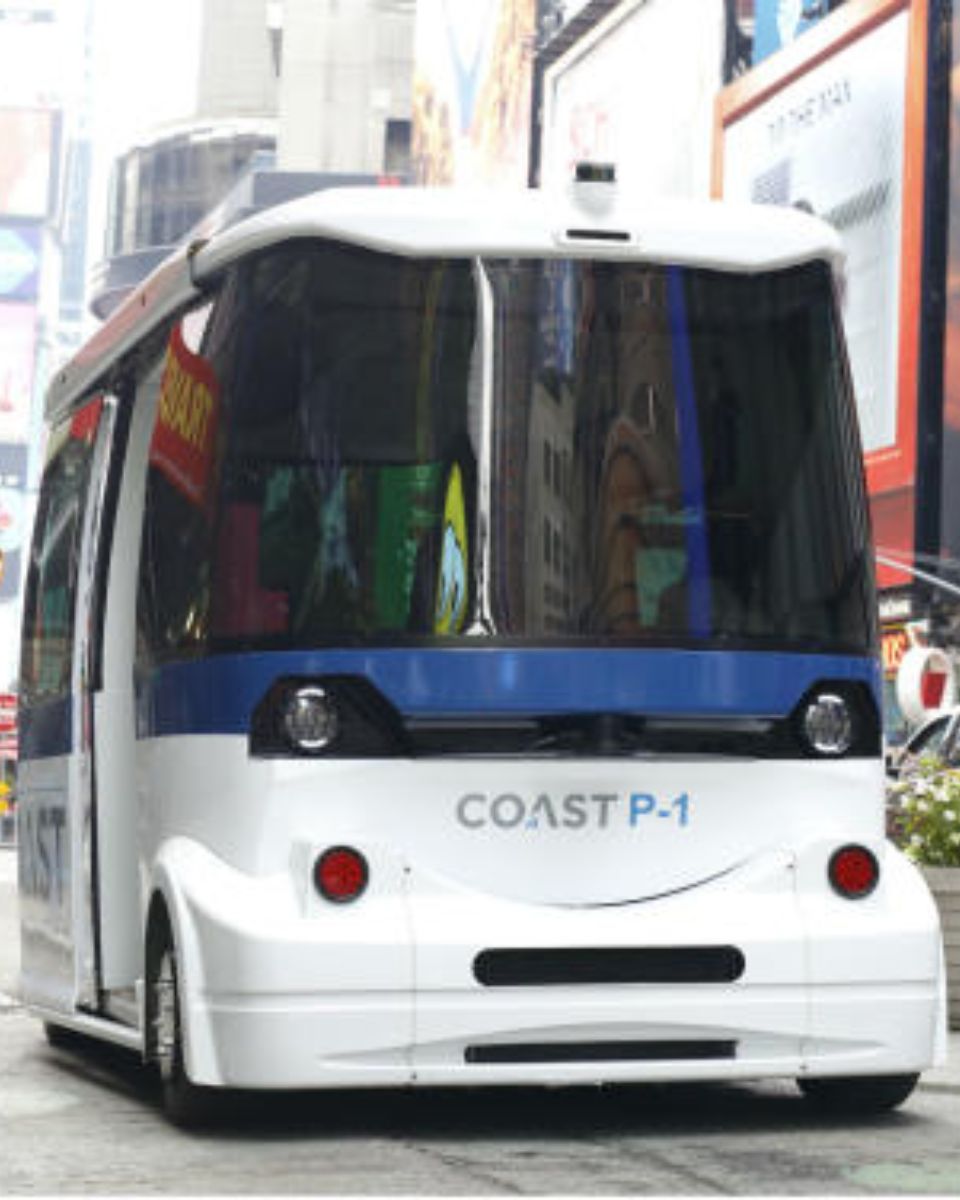
SBG Systems’ inertial navigation solutions support many autonomous vehicle applications beyond traditional passenger cars. Our sensors enable precise positioning, orientation, and motion data for unmanned ground vehicles and delivery robots. They also serve autonomous shuttles and industrial machines with real-time performance. Even in GNSS-denied environments, our technology ensures reliable navigation and control.
Do you have questions?
Welcome to our FAQ section! Here, you’ll find answers to the most frequent questions about the ADAS systems application we highlight. If you don’t find what you’re looking for, feel free to contact us directly!
What is the difference between ADAS in cars and self-driving cars?
ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) enhances driving safety by providing features like lane-keeping, adaptive cruise control, and automatic braking, but requires active driver supervision. In contrast, self-driving cars, equipped with autonomous driving systems, aim to fully automate vehicle operation without human intervention.
While ADAS supports drivers by assisting with tasks and improving safety, self-driving cars are designed to handle all aspects of autonomous driving, from navigation to decision-making, offering a higher level of automation (SAE levels) and convenience. ADAS characteristics or features are attributed to SAE levels below 3 and self-driving cars as such correspond to minimum level 4.





