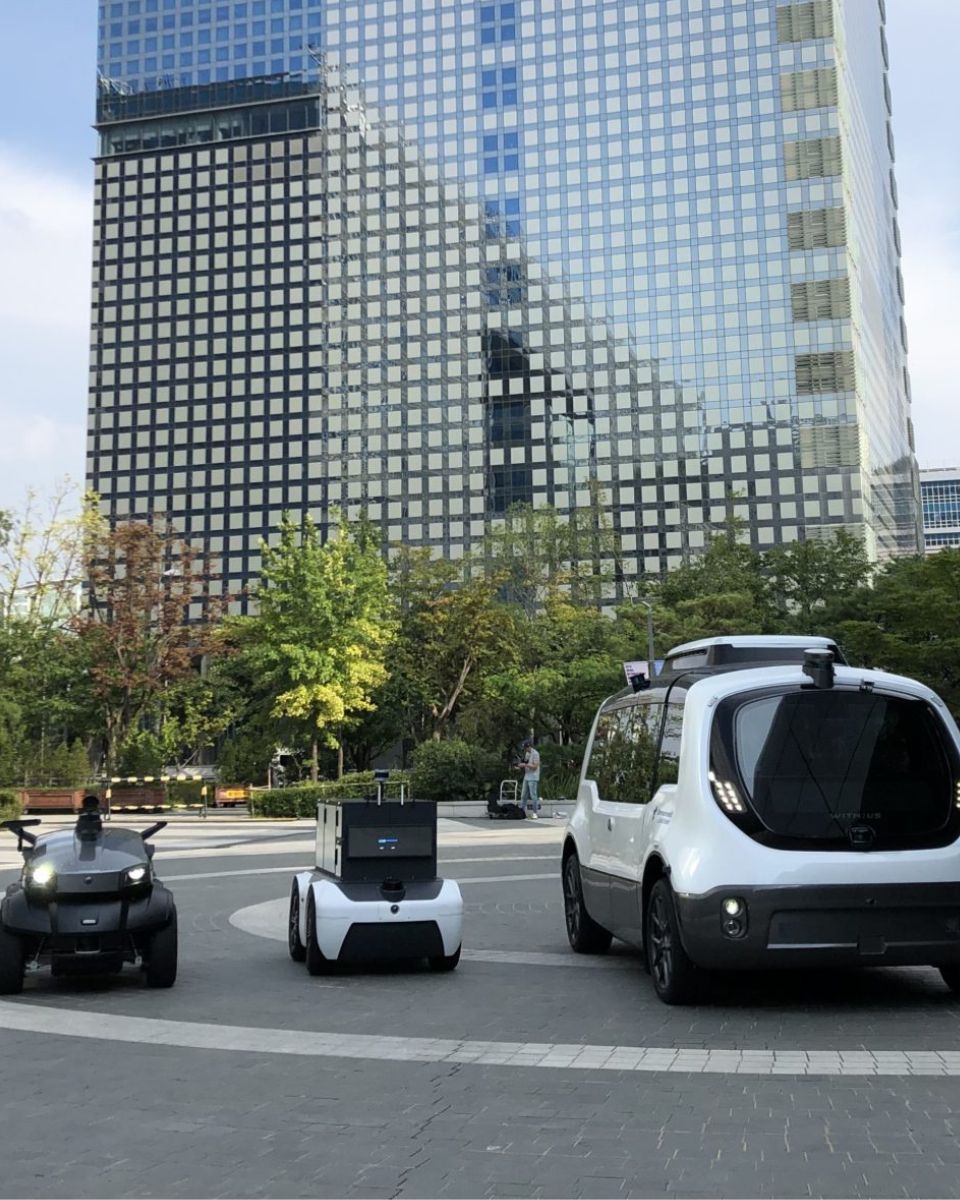
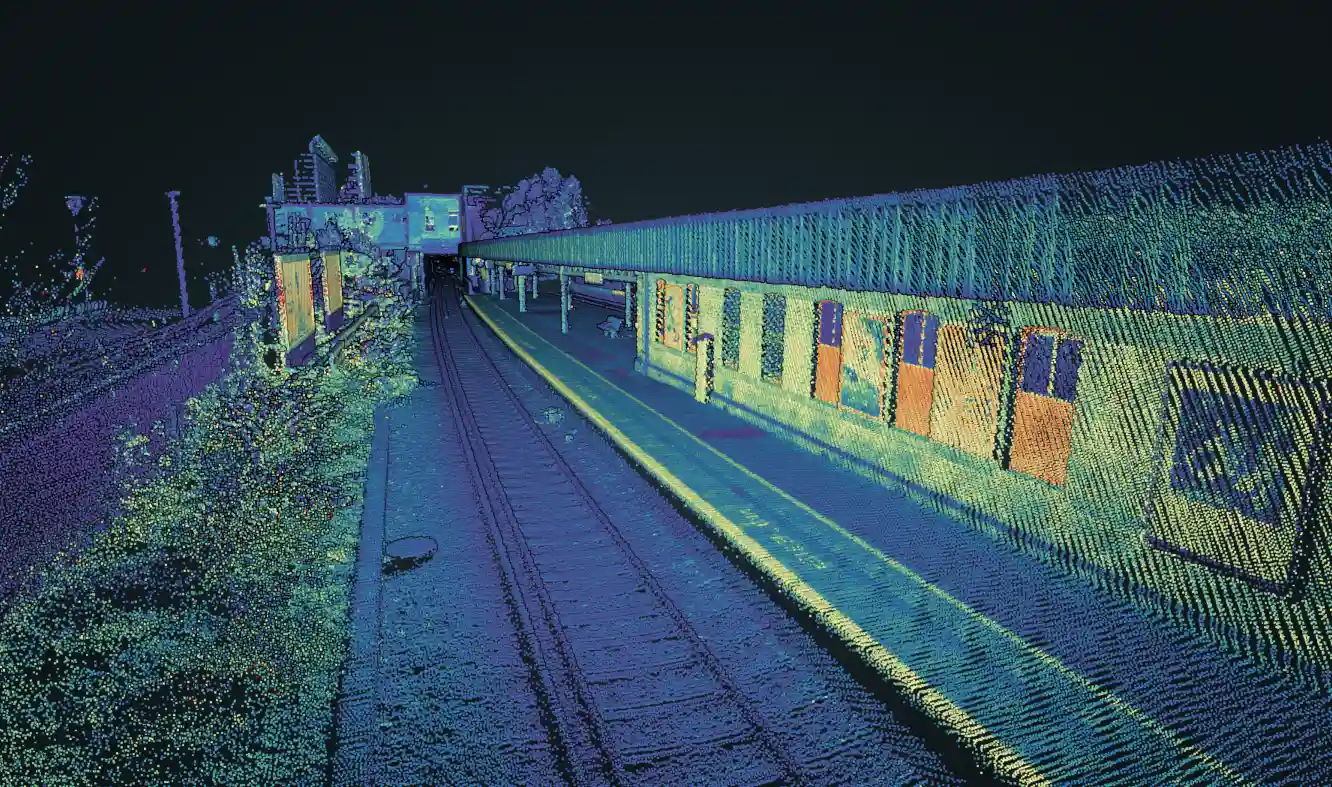
Enhancing autonomous cars navigation
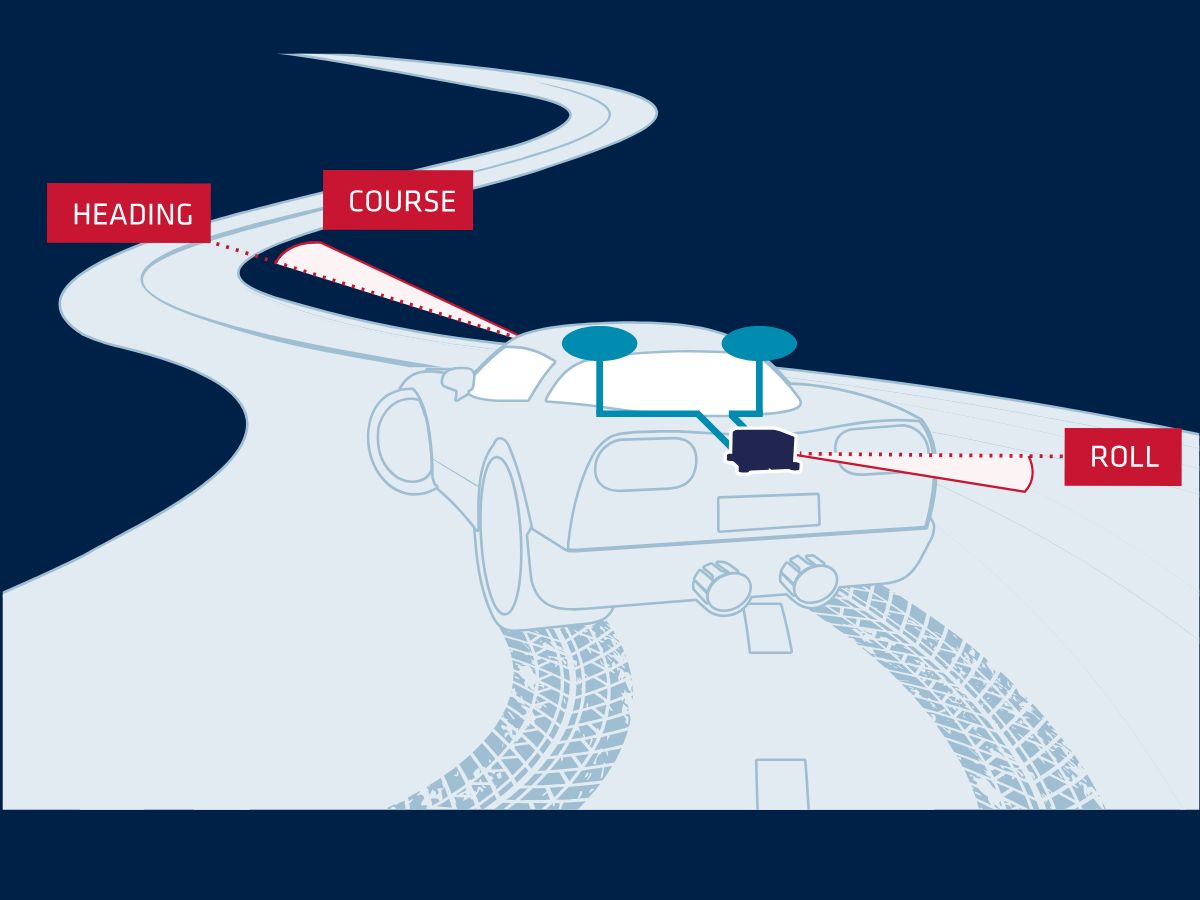
Our Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) provides real-time roll, pitch, and heading, integrated with a GNSS receiver to maintain accuracy in case of signal outages (buildings, trees, tunnel, etc.).
Inertial sensors are also used to precisely synchronize and stabilize additional equipment such as LiDAR or Camera for a driverless car application. The integration of an INS with other sensors helps create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s environment, enabling it to navigate complex and dynamic scenarios with greater precision.

Improving safety and reliability of self-driving vehicles
One of the most challenging environments for self-driving cars is urban areas, where GNSS signals can be obstructed by tall buildings, and traffic conditions can change rapidly. INS provides the accuracy and reliability needed to navigate these environments safely.
Our INS sensors use Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS) technology. This allows smaller, more accurate, and more power-efficient sensors, enhancing the overall performance of INS in autonomous cars.
Inertial navigation systems for self-driving cars
Our Inertial Navigation Systems are engineered to provide the unrivaled accuracy and reliability required to navigate complex environments, like urban canyons, with confidence.
We created advanced INS solutions that integrates seamlessly with your autonomous vehicle systems, delivering real-time data that ensures precise positioning and smooth, accurate control. From urban streets to challenging terrains, we empower your self-driving car technology with the robust, high-performance navigation capabilities needed to achieve safe, reliable, and efficient autonomous operation.
Our solutions for self-driving cars
Drive the future of autonomous mobility with us, where innovation meets precision, and every journey is guided with unparalleled accuracy. Discover our solutions for self-driving cars navigation.
Autonomous applications brochure
Get our brochure delivered straight to your inbox!
Explore other potential applications for autonomous vehicles
Autonomous vehicles are transforming industries far beyond transportation. From agriculture and logistics to construction and surveillance, advanced navigation technologies are enabling smarter, safer, and more efficient operations. Explore the wide range of innovative applications powered by autonomy.
Do you have questions?
Find answers to the most common questions about the applications we showcase. If you don’t find what you’re looking for, feel free to contact us directly!
How self-driving cars work?
Self-driving cars are vehicles equipped with sophisticated systems that enable them to navigate and control themselves without human intervention. These vehicles use a combination of autonomous driving sensors and algorithms to perceive their environment, make decisions, and perform self driving tasks. The goal is to achieve full autonomy, where the vehicle can handle all aspects of driving safely and efficiently.
Self-driving cars rely on an array of key technologies to perceive their surroundings. These include:
- GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System): to get the real-time updates on the self-driving car position, speed, and direction.
- INS (Inertial Navigation Systems): to maintain accuracy in case of GNSS signal outages. It provides real-time updates on the self driving car position, speed, and direction.
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): use of laser beams to create a detailed 3D map of the vehicle’s environment. This technology helps the car detect and measure objects around it, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and road signs.
- Radar (Radio Detection and Ranging): use of radio waves to detect the speed, distance, and direction of objects. Radar is particularly useful in adverse weather conditions and for detecting objects at longer ranges.
- Cameras: to capture visual information about the vehicle’s environment, including lane markings, traffic signals, and road signs. They are essential for interpreting complex visual cues and making decisions based on visual data.
What is the difference between ADAS in cars and self-driving cars?
ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) enhances driving safety by providing features like lane-keeping, adaptive cruise control, and automatic braking, but requires active driver supervision. In contrast, self-driving cars, equipped with autonomous driving systems, aim to fully automate vehicle operation without human intervention.
While ADAS supports drivers by assisting with tasks and improving safety, self-driving cars are designed to handle all aspects of autonomous driving, from navigation to decision-making, offering a higher level of automation (SAE levels) and convenience. ADAS characteristics or features are attributed to SAE levels below 3 and self-driving cars as such correspond to minimum level 4.






