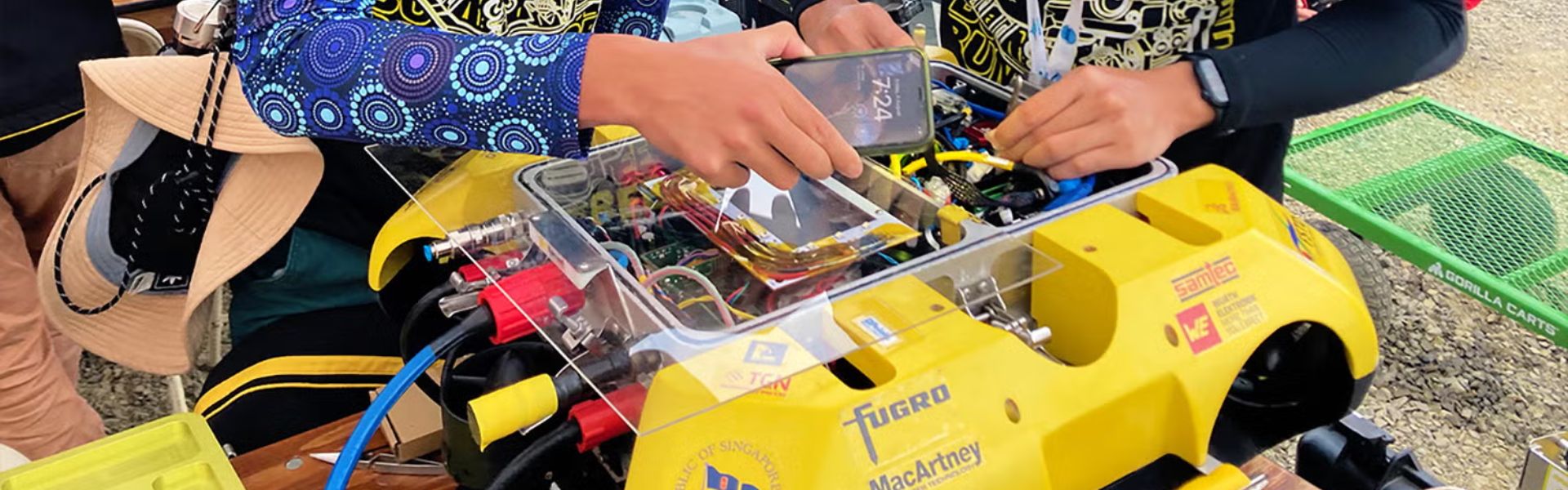
Robots sweep awards with our sensors
“SBG Systems’ products are top of the line, providing all the accuracy and precision we need. Importantly, the documentation and support are top notch, which is especially beneficial for students like us. A shout out to Mr. Jérémy Colombel and Mr. Nicolas Michel here in Singapore who has been especially helpful to us.” | Isabella Lu, Electrical Engineer, Team Bumblebee
Team Bumblebee is a group of innovative students from the College of Design and Engineering (CDE), School of Computing (SoC), and the NUS Business School at the National University of Singapore (NUS). Their vision is to build autonomous systems of the future.
Their focus is on designing and building autonomous maritime vehicles capable of navigating both underwater and on the water surface.
The team consists of students from diverse backgrounds, including Mechanical, Computer, Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, and Business.
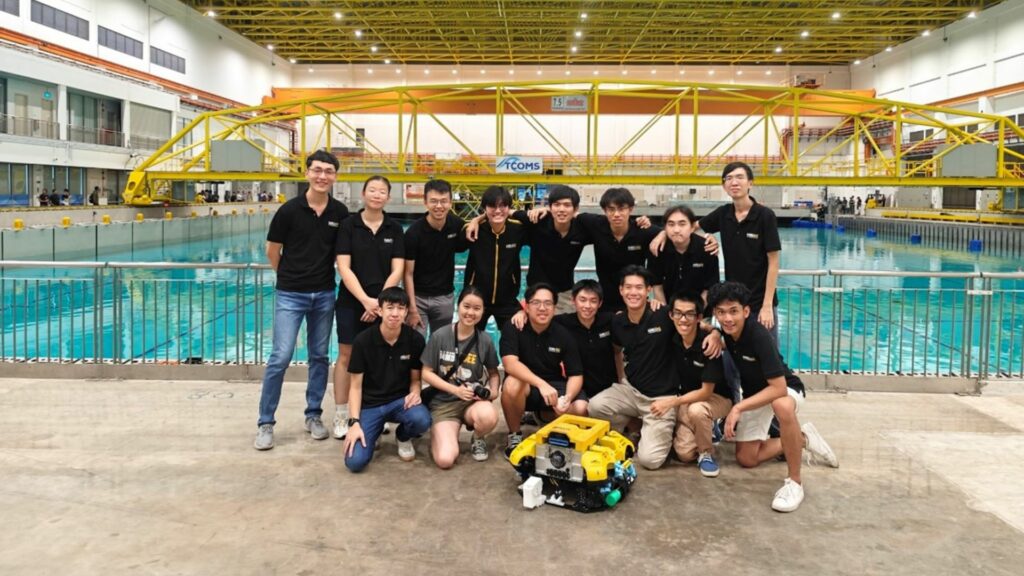

Team Bumblebee’s current system comprises three autonomous-capable vehicles: BBAUV4.1 (Autonomous Underwater Vehicle), ASV 3.0 (Autonomous Surface Vessel), and Jellyfish (Unmanned Aerial Vehicle).
These vehicles have achieved remarkable success in international competitions, such as the RoboSub Challenge and RobotX.
A need for accurate and robust INS
Team Bumblebee needed a high-precision, robust, low-latency IMU with a GPS unit to achieve precise localization and navigation in a maritime environment. Their key requirements included:
- Less than 1-degree Roll & Pitch accuracy.
- Compatibility with Ubuntu, preferably with an ROS driver or readily available third-party driver.
- Adequate in-built magnetic shielding to prevent interference.
- Robust and standard connectors.
- Support for RTK (Real-Time Kinematic) positioning.
These sensors would be mounted on a modified WAM-V platform used for autonomous missions in the maritime environment, enabling navigation, obstacle avoidance, object detection, and mission planning.
Why team Bumblebee chose SBG Systems?
Team Bumblebee conducted a thorough evaluation of various IMU providers. They decided to partner with SBG Systems due to several key factors:
1 – Weather-resistant casing: SBG Systems’ sensors came with IP-68 weather-resistive casings, making them suitable for maritime applications.
2 – Manufacturer’s credibility: SBG Systems’ reputation in the field of inertial sensors and navigation systems played a significant role in their decision.
3 – Technical advancements: SBG Systems’ Ellipse-D sensor offered advanced features, including dual-antenna GPS and improved heading data, reducing the need for magnetometer calibration.
4 – Expert support: Team Bumblebee received valuable technical advice from the experts who were consistently available to assist.
Accurate orientation and strong support
After integrating SBG Systems’ Ellipse-D into their systems, team Bumblebee experienced significant improvements:
- Dual antenna GNSS: The addition of dual antenna GNSS eliminated the influence of magnetic interference, providing accurate orientation data and absolute yaw readings, crucial for navigation above water bodies.
- Gyro calibration: The team received support from SBG Systems’ engineers to address gyro bias issues and ensure stable performance.
A perfect match
Ellipse-D perfectly matched team Bumblebee’s ASV application constraints, providing the required accuracy, robustness, and ease of integration.
Team Bumblebee appreciated several benefits of using SBG Systems’ products:
✦ Prompt support: The support team provided timely assistance when needed.
✦ Detailed documentation: Comprehensive data sheets and application guides were available, aiding in integration and troubleshooting.
✦ Ease of integration: SBG Systems’ sensors were designed with mounting holes and plug-and-play USB connectivity, simplifying integration.
✦ Discounted pricing: The cost-effective pricing was beneficial for a student-led project.
✦ Waterproof and durable casing: The weather-resistant casings of SBG Systems’ sensors contributed to their durability in maritime environments.
Three things team Bumblebee loves about us
1 – Sincerity and commitment: SBG Systems demonstrated a remarkable commitment to supporting team Bumblebee beyond a typical supplier-client relationship, going the extra mile to assist the team’s success.
2 – Engineers’ passion and dedication: The passion and knowledge of SBG Systems’ support engineers resonated with team Bumblebee’s love for robotics and technology.
3 – Ample documentation and support: The extensive documentation and support, along with the assistance from the sales team, made the integration process smoother for the student team.
Bumblebee recently participated in the Maritime Robosub Challenge 2023 held at the US Naval Transdec facility in San Diego, California with a total of 35 teams from 5 countries. They emerged as Champions, along with the other listed accomplishments below.
RoboSub 2023 Awards:
- 1st Place in Autonomy Challenge
- 1st Place System Assessment
- 1st Place Website
- 2nd Place Design Documentation
SBG Systems extends its best wishes to team Bumblebee for all their future endeavors.

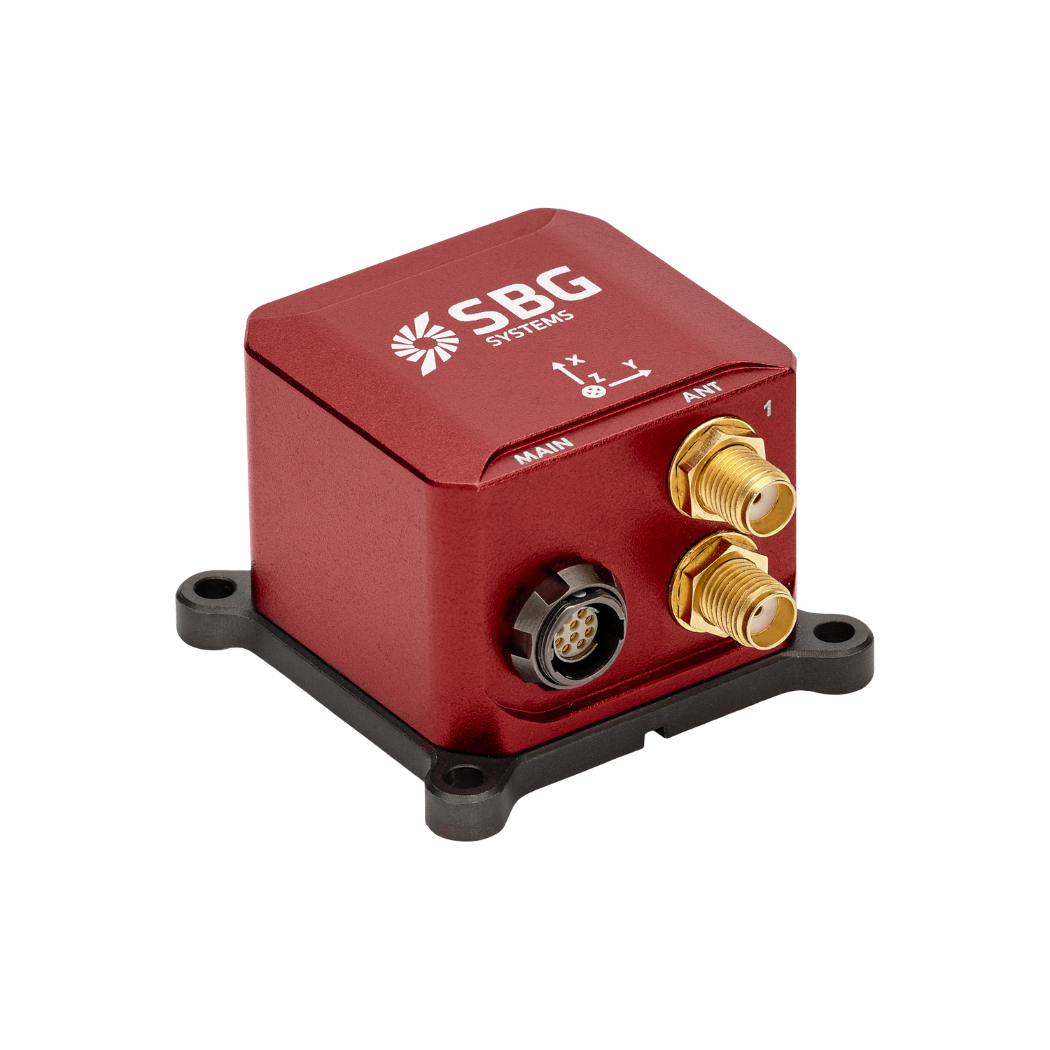
Ellipse-D
The Ellipse-D is an inertial navigation system integrating a dual antenna and dual frequency RTK GNSS that is compatible with our Post-Processing software Qinertia.
Designed for robotic and geospatial applications, it can fuse Odometer input with Pulse or CAN OBDII for enhanced dead-reckoning accuracy.

Ask a quotation for Ellipse-D
Do you have questions?
Welcome to our FAQ section! Here, you’ll find answers to the most common questions about the applications we showcase. If you don’t find what you’re looking for, feel free to contact us directly!
What is the inertial guidance system of a USV?
An inertial guidance system for an Unmanned Surface Vehicle (USV) is crucial for precise navigation and control, especially when GNSS is unavailable. Inertial sensors track motion and orientation, enabling effective navigation in challenging environments.
Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) integrate IMU data with other systems, such as GNSS or Doppler Velocity Logs, for enhanced accuracy. They also employ navigation algorithms, such as Kalman Filtering, to calculate position and velocity.
Inertial sensors support autonomous operation, providing accurate heading and position data for various applications. They ensure effective operation in GNSS-denied conditions and allow real-time adjustments for enhanced maneuverability.
What is the difference between IMU and INS?
The difference between an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) and an Inertial Navigation System (INS) lies in their functionality and complexity.
An IMU (inertial measuring unit) provides raw data on the vehicle’s linear acceleration and angular velocity, measured by accelerometers and gyroscopes. It supplies information on roll, pitch, yaw, and motion, but does not compute position or navigation data. The IMU is specifically designed to relay essential data about movement and orientation for external processing to determine position or velocity.
On the other hand, an INS (inertial navigation system) combines IMU data with advanced algorithms to calculate a vehicle’s position, velocity, and orientation over time. It incorporates navigation algorithms like Kalman filtering for sensor fusion and integration. An INS supplies real-time navigation data, including position, velocity, and orientation, without relying on external positioning systems like GNSS.
This navigation system is typically utilized in applications that require comprehensive navigation solutions, particularly in GNSS-denied environments, such as military UAVs, ships, and submarines.
