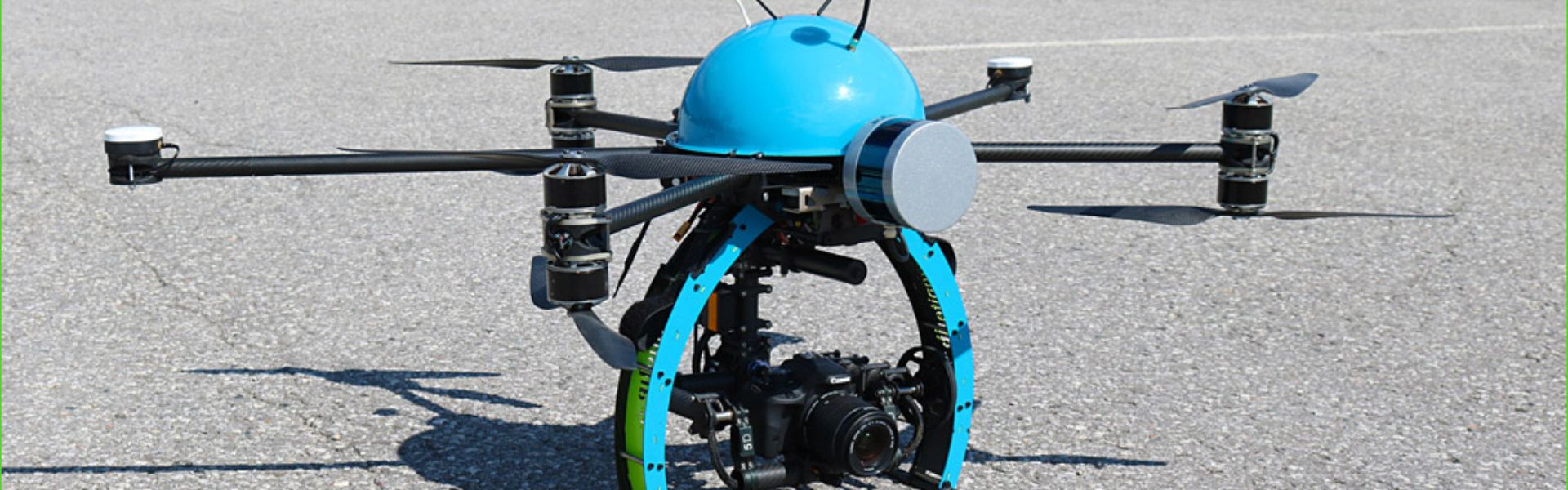
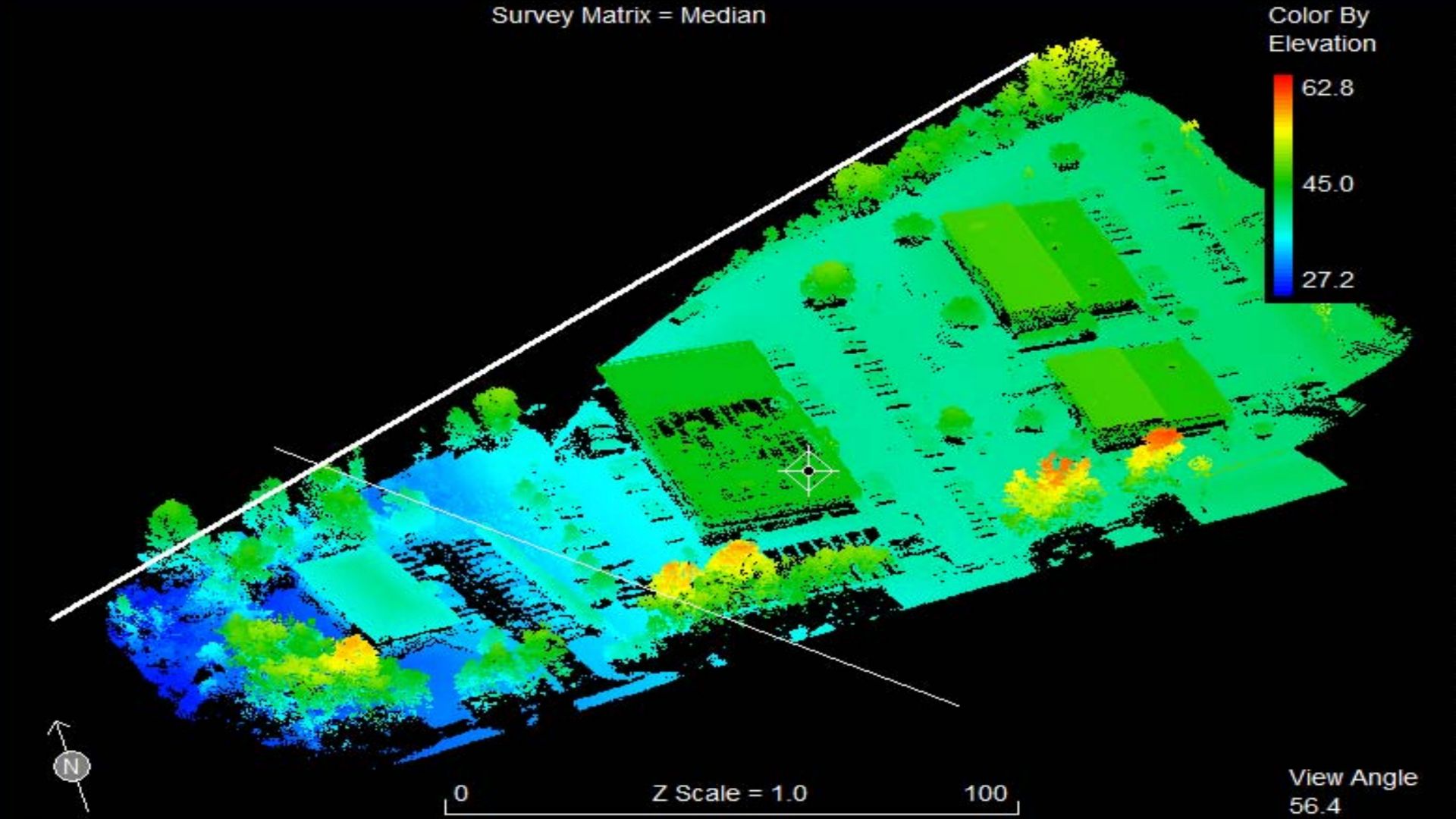
UAV LiDAR motion compensation and georeferencing
Hypack chose the Ellipse-D inertial navigation system to equip their new UAV-based surveying solution: the NEXUS 800.
“The Ellipse-D has an amazing SWP (small Size – low Weight – low Power) ratio”. | Hypack
New UAV-based surveying solution
The NEXUS 800 powered by HYPACK is a full end-to-end solution that represents a new paradigm in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) data collection by seamlessly harmonizing LiDAR data with photogrammetry.
Powered by HYPACK-HYSWEEP mapping software, the operator can plan, acquire, and process the LiDAR and Photogrammetry data onboard a high powered Windows PC and high performance UAV allowing for rapid analysis, product creation and export to a variety of CAD and GIS formats.
NEXUS 800 equipped with Ellipse-D INS
The NEXUS 800 features:
- Provides a full GNSS aided inertial navigation system with the Ellipse-D INS
- Visualizes LiDAR return with a 360 degree field of view
- Acquires LiDAR and Photogrammetric data using the powerful and user-friendly HYPACK-HYSWEEP software
- Displays Real-Time photogrammetry and Point Cloud viewing
- Provides Point Cloud and georeferenced photogrammetry correlation via post processing
- Includes an On-board Windows® PC for rapid data processing and product creation
- Allows volume computations and data analyses
- Includes a comprehensive full flight system, training and support
The NEXUS 800 UAV represents Hypack commitment to the surveying and mapping community seeking a true end-to-end solution leveraging the various expertise from HYPACK, Infinite Jib, SBG Systems, and Velodyne onto one compact solution.
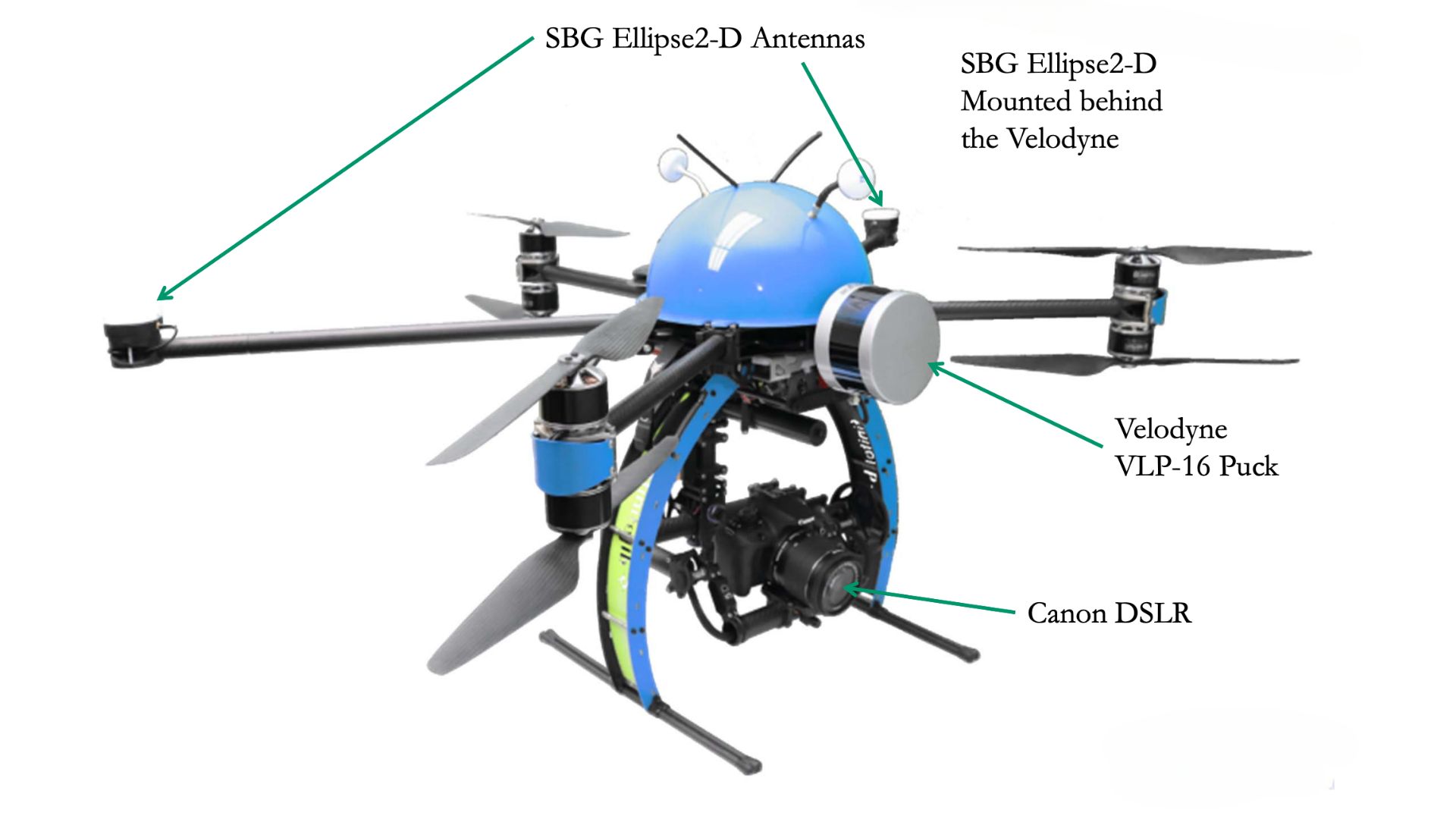
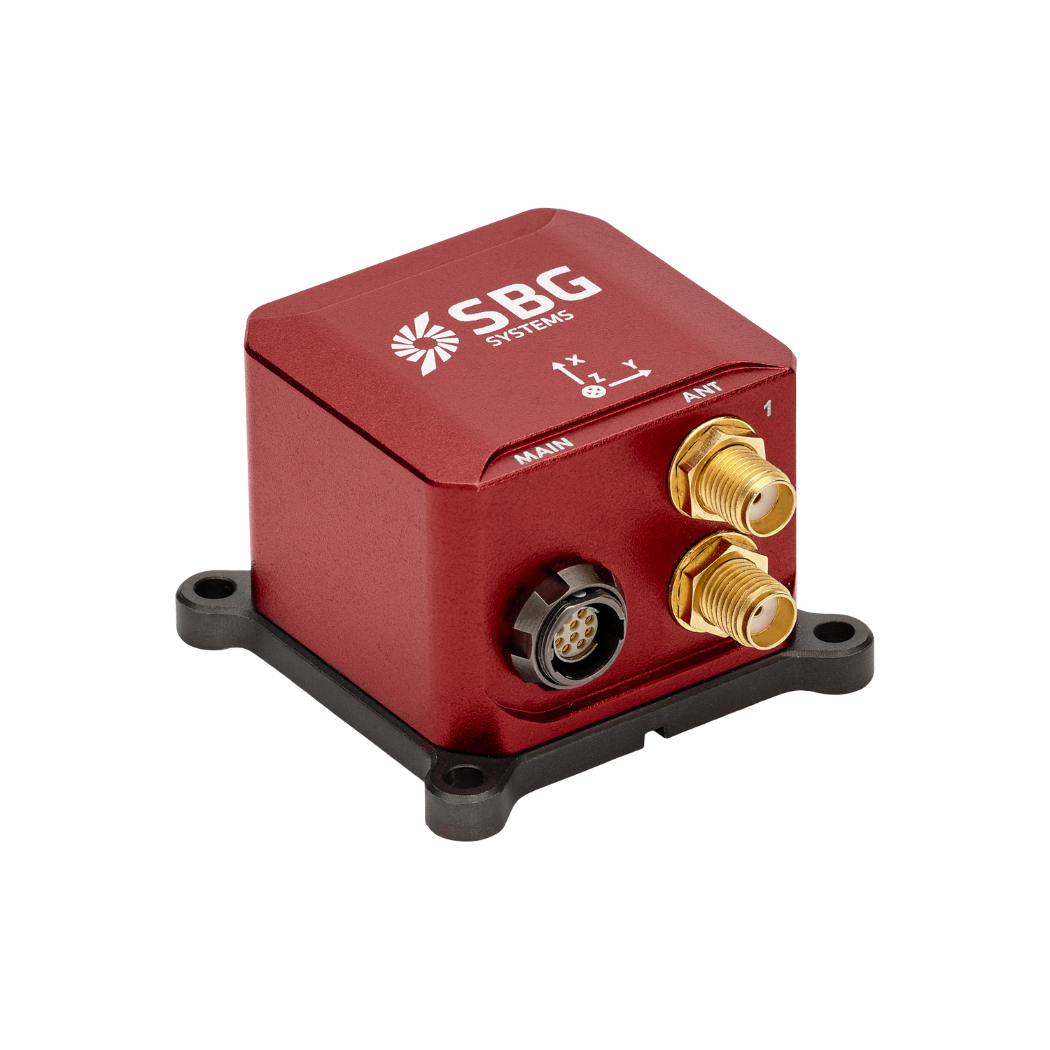
Ellipse-D
The Ellipse-D is an inertial navigation system integrating a dual antenna and dual frequency RTK GNSS that is compatible with our Post-Processing software Qinertia.
Designed for robotic and geospatial applications, it can fuse Odometer input with Pulse or CAN OBDII for enhanced dead-reckoning accuracy.

Ask a quotation for Ellipse-D
Do you have questions?
Welcome to our FAQ section! Here, you’ll find answers to the most common questions about the applications we showcase. If you don’t find what you’re looking for, feel free to contact us directly!
Do UAVs use GPS?
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, typically use Global Positioning System (GPS) technology for navigation and positioning.
GPS is an essential component of a UAV’s navigation system, providing real-time location data that enables the drone to determine its position accurately and execute various tasks.
In recently years, this term has been replaced by a new term GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System). GNSS refers to the general category of satellite navigation systems, which encompasses GPS and various other systems. In contrast, GPS is a specific type of GNSS developed by the United States.
What is a payload?
A payload refers to any equipment, device, or material that a vehicle (drone, vessel …) carries to perform its intended purpose beyond the basic functions. The payload is separate from the components required for the vehicle operation, such as its motors, battery, and frame.
Examples of Payloads:
- Cameras: high-resolution cameras, thermal imaging cameras…
- Sensors: LiDAR, hyperspectral sensors, chemical sensors…
- Communication equipment: radios, signal repeaters…
- Scientific instruments: weather sensors, air samplers…
- Other specialized equipment
What is UAV geofencing?
UAV geofencing is a virtual barrier that defines specific geographic boundaries within which an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) can operate.
This technology plays a critical role in enhancing the safety, security, and compliance of drone operations, particularly in areas where flight activities may pose risks to people, property, or restricted airspace.
In industries like delivery services, construction, and agriculture, geofencing helps ensure that drones operate within safe and legal areas, avoiding potential conflicts and enhancing operational efficiency.
Law enforcement and emergency services can use geofencing to manage UAV operations during public events or emergencies, ensuring drones do not enter sensitive areas.
Geofencing can be employed to protect wildlife and natural resources by restricting drone access to certain habitats or conservation areas.
What is georeferencing in aerial surveying?
Georeferencing is the process of aligning geographic data (such as maps, satellite images, or aerial photography) to a known coordinate system so that it can be accurately placed on the Earth’s surface.
This allows the data to be integrated with other spatial information, enabling precise location-based analysis and mapping.
In the context of surveying, georeferencing is essential for ensuring that the data collected by tools like LiDAR, cameras, or sensors on drones is accurately mapped to real-world coordinates.
By assigning latitude, longitude, and elevation to each data point, georeferencing ensures that the captured data reflects the exact location and orientation on the Earth, which is crucial for applications such as geospatial mapping, environmental monitoring, and construction planning.
Georeferencing typically involves using control points with known coordinates, often obtained through GNSS or ground surveying, to align the captured data with the coordinate system.
This process is vital for creating accurate, reliable, and usable spatial datasets.
