Motion Reference Unit (MRU) is a sensor system designed to measure and report the dynamic movements of an object, particularly in marine and aerospace environments. These units provide data on roll, pitch, and heave motions, which are crucial for navigation, stabilization, and operational efficiency. MRUs utilize advanced sensor technologies to deliver high-precision motion data in real-time.
These devices find application in various vessels, including ships and aircraft, as well as industrial platforms, where they contribute to the maintenance of operational safety under conditions of constant motion.
An MRU is sometimes referred to as an Attitude & Heading Reference System (AHRS) or Vertical Reference Unit (VRU) , but they serve different purposes. An AHRS provides full 3D orientation, including heading, and engineers frequently use it for navigation. A Motion Reference Unit focuses on motion dynamics, especially vertical motion such as heave. Operators often use it for marine stabilization and motion compensation.
To optimize heave performance:
- Place the sensor near the center of rotation and clearly define the point of interest, such as mounting it directly on top of the MBES sonar using a “Monitoring Point”. Note that only heave measurements can be transferred; surge and sway must remain measured at the IMU.
- Alternatively, position the sensor in a more accessible location or closer to the point of interest. Then properly configure the Main Lever Arm (COR) and the monitoring point.

Technologies behind MRUs
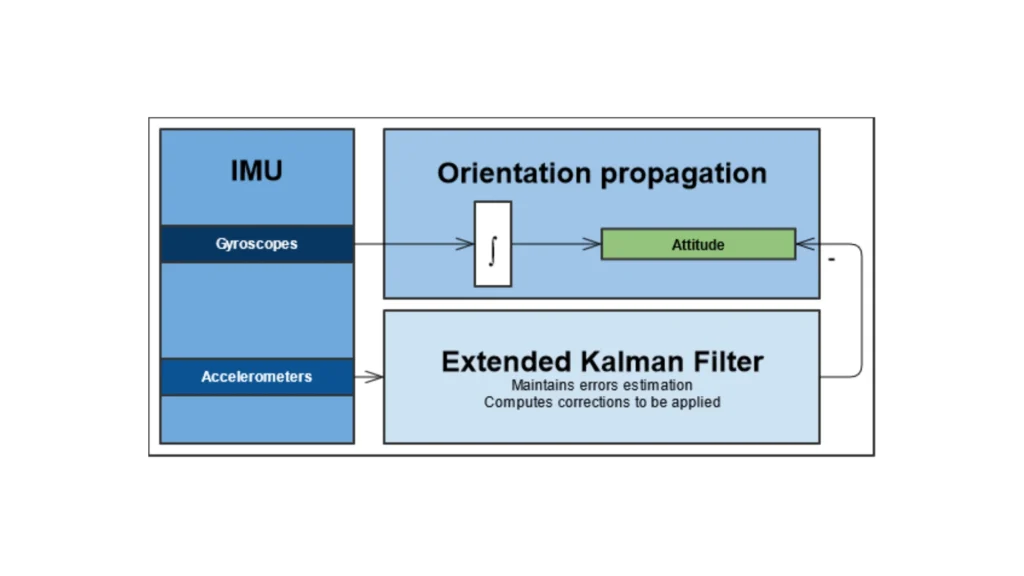
The fundamental component of an MRU is the Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), which comprises gyroscopes and accelerometers. Gyroscopes are instruments that detect rotation around different axes and provide precise angular velocity data.
High-end MRUs frequently utilise fibre optic or ring laser gyroscopes to ensure optimal stability and precision.Accelerometers are capable of measuring linear acceleration, thereby enabling the tracking of motion along the X, Y, and Z axes. The majority of MRUs also incorporate GNSS technology with a view to enhancing positional accuracy and stability.
RTK and differential GNSS corrections further refine motion tracking by reducing signal errors. The utilisation of advanced data fusion algorithms by a motion reference unit is pivotal in the consolidation of sensor inputs into a unified, coherent output. Kalman filters remove noise and improve measurement accuracy across all motion parameters.
Sensor fusion algorithms combine gyroscope, accelerometer, and GNSS data to ensure more reliable motion tracking.
Applications of motion reference units
In marine applications, a motion reference unit helps stabilize ships and improve dynamic positioning systems. Furthermore, they assist in the rectification of vessel motion during hydrographic surveys, thereby enhancing the precision of seabed mapping. In the field of aerospace engineering, MRUs play a pivotal role in the control of UAVs, the stability of aircraft, and the management of satellite orientation.
The offshore and subsea industries utilise MRUs to guide ROVs and stabilise drilling platforms. In the domain of civil engineering, MRUs play a pivotal role in the monitoring of structural movement and the guidance of precision equipment on dynamic sites. These units function in a continuous manner, thereby providing data that supports safety, accuracy, and efficient operation. As technology advances, MRUs or VRUs will continue to evolve in order to meet the increasing demand for precise motion data.
If you have a project in mind that involves Motion Reference Unit solutions, please get in touch with our experts.
Tell us about your project