Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) are fundamental components in modern navigation and motion tracking systems.
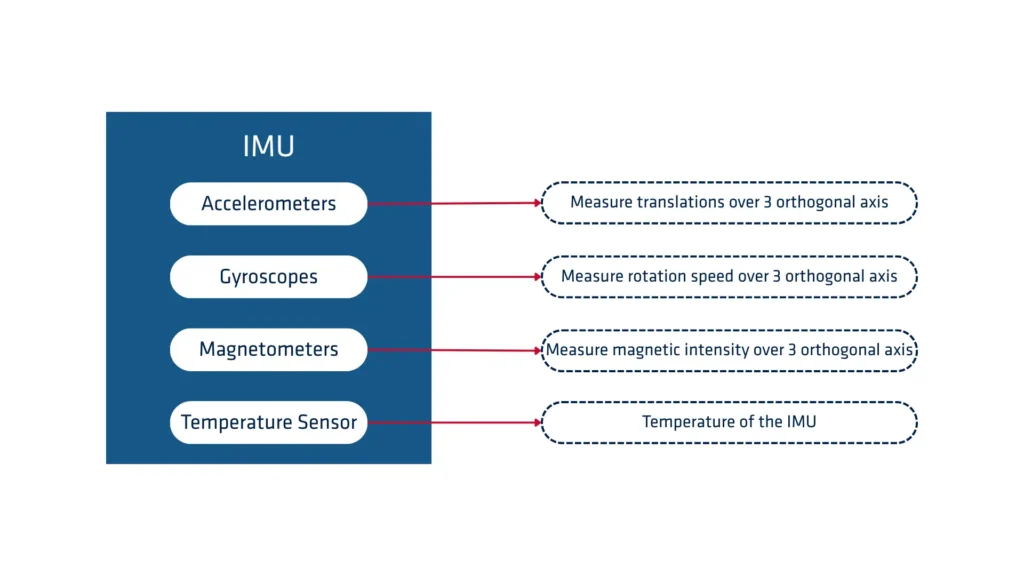
An Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body’s specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the magnetic field surrounding the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers.
IMUs are critical for tracking and controlling the position and orientation of various objects, from aircraft and ships to smartphones and gaming controllers.
There are different types of IMU sensors: the one based on FOG (Fiber Optic Gyroscope), the RLG IMUs (Ring Laser Gyroscope), and lastly, IMU based on MEMS technology (Micro Electro-Mechanical Systems). This technology allows lower costs and low power requirements while ensuring performance. MEMS-based systems therefore combine high performance and ultra-low power in a smaller unit.
The system outputs raw data at 1KHz for demanding real-time applications.
How to choose the best IMU ?
When choosing the best IMU for your needs, several factors must be considered to ensure high accuracy, reliability, and performance. The first factor is sensor accuracy, which directly impacts the precision of measurements.
High-quality IMUs have low bias, drift, and noise, ensuring that the data they provide is accurate and stable over time. Calibration is also crucial, as well-calibrated sensors minimize error accumulation, especially in dynamic environments.
The range and resolution of the IMU sensors are also important. Depending on your application, you may need an IMU with a wide dynamic range to handle extreme conditions, or one with high resolution for precise measurements in smaller motions.
Power consumption is another critical consideration, especially for battery-operated systems like drones and autonomous vehicles. A low-power IMU extends operational time and reduces energy costs, making it more efficient for long-duration missions.
Durability is essential. IMUs designed for harsh environments, such as those used in defense or aerospace, must be rugged enough to withstand temperature fluctuations, vibrations, and shocks. Additionally, consider the form factor and integration compatibility.
Smaller, lighter IMUs work best for portable devices or unmanned systems, while larger systems are required for more robust applications.
Lastly, choosing a trusted manufacturer with a proven track record in delivering high-performance IMUs ensures you get a reliable product that meets your needs for precise and accurate motion tracking.